Aim of the study: To evaluate the feasibility and to measure the effects of a six-week long adapted physical activity programme, including 5 days of intense dog sledding, on the physical and psychological health of children and adolescents treated for cancer.
Methods: Eleven children and teenagers (4 girls, 7 boys; mean age 14.3 ± 2.9 years) participated in this monocentric pilot programme of adapted physical activities from February 2013 to March 2013. Seven were still on treatment. The programme lasted 6 weeks. A series of physical tests and psychological questionnaires were carried out before and after the programme.
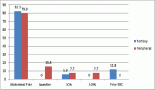
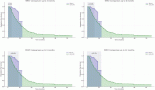
Results: All children and teenagers completed the full programme. An improvement in all physical and psychological parameters was observed. Statistically significant differences were observed for global self-esteem (6.2 ± 2.1 to 7.7 ± 1.8; p = 0.02), perceived sport competence (5.3 ± 3.2 to 7.4 ± 2; p = 0.02) and perceived physical strength (5.6 ± 2.5 to 7.1 ± 1.8; p = 0.001). Regarding physical tests, the physical training led to statistically significant improvement for sit-ups (13.8 ± 2.6 to 21.75 ± 5.4; p = 0.01), muscle tone (76 ± 23.7 to 100 ± 22.9; p = 0.01), and resting heart rate (96.1 ± 3.2 to 91.6 ± 4.5; p = 0.03).
Conclusion: This programme is feasible in children and adolescents even during their oncologic treatment. During the 6-week programme, children and adolescents improved their physical and psychological health, and the putative benefits of the adapted physical activity programme are discussed. A larger randomised trial started in 2014.