We conducted a retrospective audit of six patients with various haematological malignancies (two acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, one acute myeloid leukaemia, and three non-Hodgkin lymphoma); these patients were eligible to receive rasburicase, being at high risk of development of tumour lysis syndrome (TLS). They received a fixed single low-dose regimen of rasburicase (7.5 mg) mainly due to financial restriction, as patients were not supported by the National Health Service and did not have health insurance. We compared uric acid, creatinine levels, and electrolytes (i.e. phosphate, potassium, and calcium) before and after rasburicase administration and also assessed the need for renal replacement therapy after treatment.
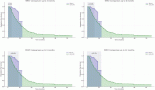
All six patients had a significant reduction in uric acid levels on the first day, achieving a response rate of 100% (p = 0.008994); creatinine, phosphate, and potassium were reduced significantly as well, with the p values of 0.0439, 0.014326, and 0.002008, respectively; only one patient needed renal replacement therapy in the form of haemodialysis, due to concerns about hyperphosphataemia.
Financial difficulties faced either because patients lacked insurance or because of the restricted National Health Service budget in Egypt have resulted in the unavailability of certain modalities of treatment in cancer care and the need to consider more economic yet efficient approaches. Our experience suggests that a single low-dose rasburicase injection (7.5 mg) is an efficient and cost-effective method to control hyperuricaemia in patients with a high risk of developing TLS when compared with the more expensive and extended standard regimen and doses recommended.