Background: The appropriate selection criteria for breast-conserving surgery (BCS) or mastectomy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) are poorly defined. The aim of this study is to analyse the incidence and prognostic factors for locoregional recurrence (LRR) in patients with breast cancer (BC) treated with NAC to develop a prognostic score to help with clinical decision-making.
Materials and methods: Using our retrospective maintained BC database, we identified 730 patients treated with NAC (327 patients treated with BCS and 403 patients treated with mastectomy) between 1998 and 2014. To identify variables associated with an increased LRR rate, we performed firstly Kaplan–Meier curves, with comparisons among groups using log-rank test, and then, significant variables were included in a multivariate analysis using Cox proportional hazards. The prognostic index was developed by assigning score 0 (favourable) or score 1 (unfavourable) for each significant variable of multivariate analysis and was created separately for patients with BCS and mastectomy.
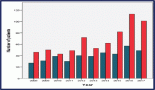
Results: At a median follow-up of 72 months, the 6-year cumulative incidence of LRR was 7.2% ( ± 3%) for BCS and 7.9% ( ± 3%) for mastectomy. By univariate analysis, variables associated with an increased LRR were for BCS: HER2 positive, grade III, ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), No-pCR (ypTis, ypN0), and age < 40 years; and for mastectomy, HER2-positive, DCIS, No-pCR, and LVI. By multivariate analysis, variables associated with an increased LRR were for BCS: HER2 positive (HR: 11.1, p = 0.001), DCIS (HR: 3.1, p = 0.005), and age < 40 years (HR: 2.8, p = 0.02); and for mastectomy: HER2 positive (HR: 9.5, p = 0.03), DCIS (HR: 2.7, p = 0.01), No-pCR (HR: 11.4, p = 0.01), and age < 40 years (HR: 2.8, p = 0.006).
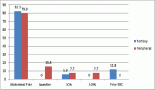
The score stratified patients into three subsets with statistically different levels of risk for LRR. For BCS, the six-year LRR rates were 3%, 13%, and 33% for the low (score 0, n = 120), intermediate (score 1, n = 95) and high (score 2–3, n = 27) risk groups, respectively (p = 0.001). For mastectomy, the six-year LRR rates were 0%, 8%, and 27% for the low (score 0, n = 20), intermediate (score 1–2, n 191), and high (score 3–4, n = 30) risk groups, respectively (p = 0.001). Of note, 21 patients that had a LRR event were HER2 positive, all of them had received trastuzumab.
Conclusions: Patients with a score of 0, which made up to 19% of the study population, had very low risk of LRR. The score enabled the identification of a small group (7%) of patients with very high risk of LRR, and who may benefit from alternative treatment.