Objective: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short regulatory RNAs that can modulate gene expression and function as negative regulators. Common genetic variants like single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in miRNA genes may alter their expression or maturation resulting in varied functional consequences in carcinogenesis. Therefore, we evaluated the genetic variants in pre-miRNAs: hsa-miR-146a G/C (rs2910164), hsa-miR-196a2 C/T (rs11614913), and hsa-miR-499 T>C (rs3746444) for their role in breast cancer susceptibility.
Study design: The study comprised 121 breast cancer patients, 115 with benign breast disease, and 164 controls. The genotypic frequency of miRNA polymorphisms was determined by PCR-RFLP assay. Logistic regression was used for statistical analysis using SPSS Software version 15.0. In silico analysis was done using various bioinformatics tools (F-SNP, FAST-SNP).
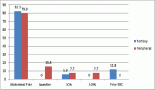
Results: The heterozygous variant of miR-146a G/C (rs2910164) is associated with the reduced risk of breast cancer at the genotype level as well as at the allele level (p < 0.05, OR = 0.5) as compared to controls. On the contrary, no significant difference was observed in the distribution of miR-196a2 C/T (rs11614913) and miR-499 T>C (rs3746444) polymorphisms in any groups both at genotype and allele levels. On the other hand, in multivariate analysis, we found that the miR-196a2 (rs11614913) C>T was associated with an increased risk of breast cancer risk in postmenopausal females (p = 0.02, OR = 3.2). We also attempted to find out the risk of malignant breast disease in relation to each of the above SNPs on dividing our data on the basis of benign and malignant status, but no significant difference was observed. In silico analysis using F-SNP showed change in transcriptional regulation by miR-146a G/C (rs2910164), miR-196a2 C/T (rs11614913) and miR-499 T>C (rs3746444) variations; the functional score was 0.100, 0.065 and 0.277, respectively.
Conclusion: The results of the present study demonstrate that miR-146a G/C (rs2910164) polymorphism is associated with reduced genetic susceptibility to breast cancer. However, multivariate analysis showed as miR-196a2 (rs11614913) C>T to be associated with increased risk of breast cancer risk in postmenopausal females. Further multicentric studies involving a large number of cases need to be carried out to strengthen the present results.