Li Fraumeni syndrome (LFS) is an inherited cancer predisposition syndrome due to TP53 gene mutation. There is sparse literature on LFS in the Indian population. We conducted a retrospective study of patients diagnosed with LFS and their family members, registered at our Medical Oncology Department between September 2015 and 2022.
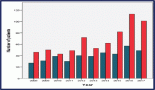
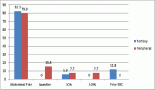
9 LFS families consisted of 29 patients diagnosed currently or historically with malignancies including 9 index cases and 20 first or second-degree relatives. Of these 29 patients, 7 (24.1%) patients developed their first malignancy before the age of 18 years, 15 (51.7%) were diagnosed between 18and and 60 years, and 7 (24.1%) were diagnosed at age more than 60 years. A total of 31 cancers occurred among the families, including 2 index cases who had metachronous malignancies. Each family had a median of three cancers (range 2–5); sarcoma (n = 12, 38.7% of total cancers) and breast cancer (n = 6, 19.3% of total cancers) being the commonest malignancies. Germline TP53 mutations were documented among 11 patients with cancers and 6 asymptomatic carriers. Of these nine mutations, the most common types were missense (n = 6, 66.6%) and nonsense (n = 2, 22.2%), and the commonest aberration was replacement of arginine with histidine (n = 4, 44.4%). Eight (88.8%) families met either classical or Chompret’s diagnostic criteria and two (22.2%) satisfied both. Two (22.2%) families fit the diagnostic criteria prior to onset of malignancy in the index cases but were untested till the index cases presented to us. Four mutation carriers from three families are undergoing screening as per the Toronto protocol. No new malignancies have been detected so far during the mean surveillance duration of 14 months.
The diagnosis of LFS has socio-economic implications for patients and their families. Delay in genetic testing misses out a crucial window wherein asymptomatic carriers could initiate surveillance in a timely fashion. Greater awareness on LFS and genetic testing in Indian patients is warranted for better management of this hereditary condition.