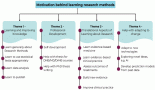
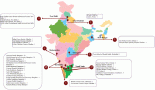
The quality and accuracy of the data provided by cancer registries has a significant impact on decision making. Over decades, high-income countries have been successful in monitoring their cancer burden because of well-established data abstraction techniques such as digital systems. Conversely, in low- and middle-income countries, sparsely distributed cancer registries, using alternative less costly, but imprecise methods are struggling to capture all cancer cases. A population-based cancer registry in South Africa covering a resource-limited rural population is faced with challenges in case finding yet the quality and accuracy of the data provided has a significant impact on decision making. The objective of this study was to assess data quality using two data quality attributes ‘completeness and accuracy’ and also to determine the benefits of using active and passive case-finding methods for cancer registration in this population. Data used were collected between January 2014 and December 2015 from four hospitals to compare the quality of both active and passive case-finding methods. From all four hospitals during the same period, a first set of data obtained through passive reporting was compared with a second set of data obtained through active case finding. Covering multiple facilities during active case finding can significantly improve quality of data, while passive case finding is challenged by data collection being confined to one specific health facility, only. Better investment in active case finding is recommended in settings with resource-distribution disparities.